Office Ergonomics - Wrist Rests
On this page
What is a wrist rest?
Back to topA "wrist rest" is a device used to support your wrists while typing (Figure 1) or when using a computer mouse (Figure 2).
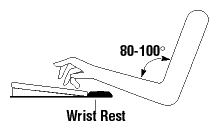
Figure 1
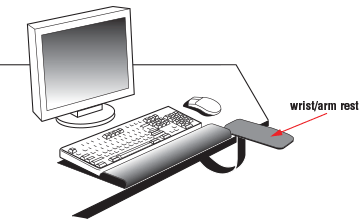
Figure 2
Do wrist rests work?
Back to topDebate surrounds the use of wrist rests for workers who keyboard and perform other repetitive tasks with their hands from a sitting position for extended periods.
On one side of the debate, it is known that leaning the wrists on a wrist rest or the edge of the desk for long periods can put a lot of pressure on the undersides of the wrists. This pressure may cause carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) to develop. On the other hand, evidence shows that wrist rests alleviate tension in the neck and shoulders.
Both views can be challenged.
Why is there a debate?
Back to topContact between the wrists and the wrist rest, if too frequent or too heavy, can indeed cause problems due to excessive pressure on the delicate tendons on the underside of the wrist, and has been known to result in CTS and tenosynovitis (inflammation of the sheath surrounding tendons). This resulting condition may be what has led people to believe that wrist rests should not be used. However, in other cases, individuals without a wrist rest would place their wrists on the sharp edges of the desk. In these cases, a softer wrist rest would help lessen the pressure.
A worker with a properly adjusted chair and desk might need only very light wrist support, if any. It is important to make sure that wrists do not rest on the desk, or too heavily on a wrist rest. However, even minimal support for the forearms or wrists with arm rests and wrist rests can take a lot of muscular tension out of the neck, shoulders and arms, without subjecting other parts of the body to unnecessary pressure or strain.
Should I get a wrist rest?
Back to topThe aim is to keep your wrists in a neutral position (not bent up or down). If used, any rest device should be selected as part of an ergonomically-designed workstation. When choosing a rest, OSHA (U.S.A.) suggests that:
- Your hands should move freely and be elevated above the wrist/palm rest while typing. When resting, the pad should contact the heel or palm of your hand, not your wrist.
- If used, wrist/palm rests should be part of an ergonomically-coordinated computer workstation
- Reduce bending of the wrists by adjusting other workstation components (chair, desk, keyboard) so the wrist can maintain an in-line, neutral posture.
- Match the wrist support to the width, height, and slope of the front edge of the keyboard (keeping in mind that the goal is to keep wrist postures as straight as possible).
- Provide wrist/palm supports that are fairly soft and rounded to minimize pressure on the wrist. The support should be at least 3.8 cm (1.5 inches) deep.
For tasks that involve working with shoulders raised, elbows held out, arms held forward and wrists held up (as in typing, micro-electronics assembly, etc.), any means of reducing muscular tension is important in preventing musculoskeletal injuries.
One's personal preference for using or not using a wrist rest is a very significant factor. Workers who choose not to use them while actually performing their tasks may opt to just use them for a rest break, between tasks. An adjustable workstation which is suited to the individual using it is essential.
- Fact sheet last revised: 2020-11-23
